Data Scientist Deep Learning Course 2025
- EIT Academy
- Dec 24, 2024
- 5 min read

Data science and deep learning have become key areas propelling innovation and automation across businesses in today's quickly changing technology landscape. Deep learning, a type of machine learning, has revolutionized a variety of jobs, from natural language processing to picture recognition. However, what precisely does a data scientist do in the field of deep learning? Let's examine the fundamental duties, abilities, and resources that characterize this fascinating field.
What is Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning that models intricate patterns in data using multi-layered neural networks. These algorithms learn from enormous volumes of data to carry out tasks like classification, regression, and generative modelling. They are inspired by the neural organization of the human brain. Deep learning applications are widely used in a variety of sectors, including healthcare, finance, and entertainment.
Examples include:
Computer Vision: Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are used by self-driving automobiles to identify things on the road.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Transformer-based models like GPT are used by virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri to comprehend speech.
Recommendation Systems: Deep learning is used by websites such as Netflix and Amazon to make tailored content recommendations.
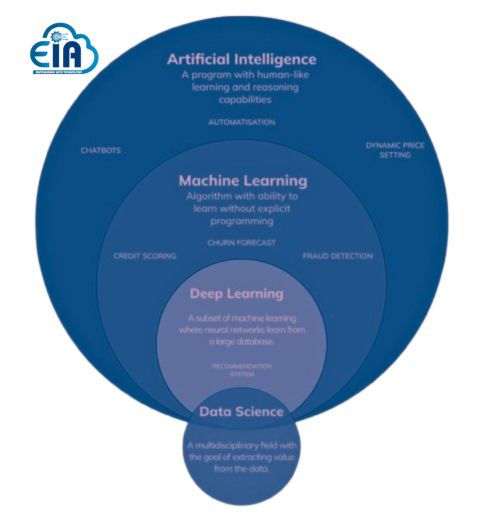
Machine Learning vs. Data Science: Key Differences
You can use the appropriate methods, resources, and knowledge to efficiently analyze and use data if you are aware of these important distinctions between data science and machine learning.

Here are some important differences to be mindful of.
Goals and Focus: Developing algorithms that let computers learn from data and make predictions is the main goal of machine learning.
Data science, on the other hand, is more broadly focused and includes a range of methods for drawing conclusions and meaning from data, such as statistical analysis and data visualization.
Utilized Technologies and Tools: Specialized libraries and frameworks are frequently used in machine learning to implement algorithms and create models.
A wider range of tools, such as statistical software, data visualization tools, and big data processing frameworks, are used in data science.
Skill Set Requirements: In order to create and improve algorithms, machine learning significantly depends on knowledge of mathematics, statistics, and programming.
A multidisciplinary skill set, including programming, statistics, data manipulation, and subject matter expertise, is necessary for data science.
Important Tasks for a Data Scientist in Deep Learning
In deep learning, a data scientist's job frequently entails establishing a connection between theoretical study and real-world implementations. The primary duties are as follows:
Problem Formulation:
Determining which business problems can be solved with deep learning methods.
Converting domain-specific issues into representations that computers can understand.
Data Preparation:
Collecting, cleaning, and preprocessing large datasets.
Balancing datasets to lessen biases and address class disparities.
Enhancing data with methods like text paraphrase and image flipping.
Model Development:
Creating neural network topologies (such as CNNs for pictures and RNNs for sequential data) that are suited to certain applications.
Adjusting hyperparameters such as activation functions, optimizers, and learning rates.
Evaluation and Optimization:
Evaluating the performance of the model with metrics like F1 score, recall, accuracy, and precision.
Adjusting models to prevent overfitting and enhance generalization.
Deployment:
Incorporating models for deep learning into operational settings.
Tracking results and retraining models in response to fresh data.
Essential Skills for a Data Scientist in Deep Learning
Mathematics and Statistics: To understand how neural networks work, one must have a solid understanding of probability, calculus, and linear algebra.
Programming Proficiency: Python proficiency is necessary because deep learning research relies heavily on frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras.
Domain Knowledge: More effective solutions are guaranteed when one is familiar with the demands and difficulties of the particular industry.
Big Data Handling: Familiarity with massive dataset management systems such as Hadoop or Apache Spark.
Soft Skills: Working with cross-functional teams requires effective communication and teamwork.
The evolution of deep learning
Interfaces between humans and machines have changed significantly over time. A newfound interest in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning is being brought about by the replacement of the mouse and keyboard with gesture, swipe, touch, and speech.
Deep learning is currently being advanced by a number of developments:
Deep learning techniques have performed better thanks to analytical advancements.
Deep learning models are now more accurate thanks to new machine learning techniques.
Novel neural network classes have been created that are ideally suited for tasks like picture categorization and text translation.
More data, such as text from social media, doctor's notes, investigation transcripts, and streaming data from the Internet of Things, can be used to create neural networks with many deep layers.
We now have access to amazing computing power because to advancements in distributed cloud computing and graphics processing units. Deep learning requires this amount of processing power to train deep algorithms.
Deep Learning Opportunities and Applications
Because deep learning methods are iterative, become more complex as the number of layers increases, and require vast amounts of data to train the networks, they require a lot of processing power to solve.
There is a chance to add more dynamic behavior to data analytics since deep learning techniques may adapt to changes in the underlying information pattern and continually improve.
The increased personalization of customer analytics is one of such options. For instance, your favorite streaming service might use your past viewing habits to generate a personalized recommendation of shows you might enjoy.
Although cognitive computing applications are currently the main focus of deep learning techniques, more conventional data analytics applications also hold a lot of promise. Take time-series analysis, for instance.
Another method deep learning can be implemented is to simply be more efficient and streamlined in existing analytical activities. Recently, SAS experimented with deep neural networks in speech-to-text transcription difficulties. When deep neural networks were used, the word-error rate dropped by over 10% when compared to the conventional methods. Additionally, neural networks removed roughly ten steps from feature engineering, modelling, and data pre-processing. The time reductions and remarkable performance improvements represent a paradigm change.
Future of Deep Learning in Data Science
Data scientists will be essential to maximizing the potential of deep learning as it develops further. Among the new trends are:
Explainable AI (XAI): Creating models that offer insights that are clear and understandable.
Federated Learning: To improve privacy, models are trained across decentralized devices.
Multimodal Learning: Integrating information from several modalities (text, images, and audio, for example) to create models that are more adaptable.
Conclusion
Data scientists are leading this revolution in deep learning, which is a frontier of opportunity. They can create significant solutions in a variety of fields by becoming proficient in deep learning methods and resources. Deep learning has countless opportunities for creativity and discovery, regardless of your level of experience as a data scientist.
FAQ
Does a data scientist do deep learning? This skill enables data scientists to develop sophisticated models that can learn from vast amounts of data
What is deep learning in data science? Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data.
Which is better, DS or ML? Each field is good for different types of people. Data scientists can help people understand data and derive insights from it, while machine learning can help people create models that improve performance using data.
Is deep learning in demand?
The global economy is booming, and there's an increasing demand for workers with expertise in artificial intelligence technology. In fact, according to some estimates, the deep learning engineer job market will grow by up to 50% by 2024. That's twice as fast as other IT jobs!








Comments